PACS has been the key to digitization for health systems and imaging centers for decades. While people working with medical images are quite familiar with this information system, there are people in the health sector, who are curious to know more about PACS and its application in the medical world.
This ultimate guide is for all those who want to have a clear understanding of PACS software, its role in patient care, and its evolution with the advent of breakthrough technologies like cloud and AI aka Artificial Intelligence.
Table of contents:
1. What is PACS
2. Essential components of PACS setup
4. Advantages of using PACS in radiology
6. Which is the right PACS solution for my institution
7. Impact of choosing the PACS solution
Suggested Read: Things You Should Know Before Implementing PACS Radiology System
1. What is PACS
Let’s start with the basics first. PACS, which is the acronym for “Picture Archiving and Communications System”, is a medical imaging software developed for radiologists and physicians for the electronic storage of images and reports. Before the advent of PACS, medical images of any modality were visualized by printing film jackets and shared through CDs and pen drives.
But now, health systems can visualize any imaging modality on their desktop or laptop screen from any location, without Pendrive and CDs, all because of PACS.
PACS has enabled easy shifting from paper to digital and eliminated manual filing, retrieving, and transporting film jackets. Apart from easy sharing of images, it also facilitates better visualization of medical images with image manipulation features like zoom, pan, flip, reset, etc.
2. Essential components of a PACS setup
Typically, a PACS system consists of the following components:
* Imaging modalities – systems that are used to scan a patient to produce medical images like x-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, etc.
* A secure network to upload and share the images safely
* A workstation that allows radiologists and physicians to read the images
* A secure storage unit to store and access patient images and other information
3. PACS vs. RIS vs. DICOM
There is an age-long confusion about PACS, RIS, and DICOM – the most common jargon of radiologists. Often PACS and RIS are interchangeably used, as people are unaware of the difference between the two.
Here’s a clear-cut description of PACS, RIS, and DICOM, that will help you understand the differences between the jargon:

3.1. PACS
PACS, as we discussed earlier, mainly serves the purpose of storing and sharing diagnostic imaging files, both 2D and 3D.
PACS was invented to create a paperless radiology practice and simplify medical image management. Medical images are an inherent part of diagnostics in current healthcare practices.
So the absence of PACS in today’s healthcare climate would mean, radiologists and healthcare professionals spending a great deal of time, if not their entire time physically storing, sharing, and retrieving the exponentially increasing medical images.
3.2. RIS
RIS or Radiology Information System on the other hand is a radiology-specific software solution that is widely used throughout the healthcare sector for optimizing radiology workflows.
Though PACS and RIS sound the same, the key difference between the two is that PACS is designed for medical image management, whereas RIS is designed for patient information management.
Here’s how RIS can optimize patient information management for health systems:
3.2.1. Patient scheduling and tracking
RIS software applications allow clinicians to easily access patient medical history, monitor treatment status, organize appointments, and process patient registrations. Furthermore, RIS systems facilitate the automation of booking processes, which accounts for most of the paper-based documentation. By automating booking processes, health systems can save a considerable amount of radiologists’ time spent on paperwork.
3.2.2. Document Management
As RIS softwares are constantly updated, patient data stays integrated and readily accessible for clinicians. Even more, using RIS systems, clinicians can generate interactive documents that can improve inter-physician communication and facilitate timely diagnosis.
3.2.3. Billing and reporting
RIS systems play a major role in optimizing billing and reporting associated with radiology procedures by allowing clinicians to store financial records, perform data analytics, automate billing, and process electronic payments.
3.2.4. Image identification
We all know that medical images are not colorful, like there are no other colors other than black, gray, and white. This is exactly why it is easy for patient images to get mixed up.
RIS systems help in correctly assigning patient data to the appropriate images, thereby facilitating easy identification of patient images and reducing the risk of study mix-ups.
By improving patient information management, RIS systems aim to streamline the diagnostic process in radiology and thereby improve accuracy and reduce patient waiting time.
3.3. DICOM
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine or simply DICOM, is entirely different from the other two.
DICOM is a widely recognized communication and management standard established to integrate different radiology imaging systems and equipment used in digital radiology.
DICOM is both a format type as well as a communication standard that ensures medical images under the format (medical image, patient information, etc.) remain intact. DICOM enables a quicker diagnostic process by easier patient data sharing between clinicians. Without the DICOM standard, healthcare professionals will take hours to complete routine tasks, even the simple ones such as comparing a patient’s medical images from different scan dates.
When images are saved in DICOM format, it is referred to as DICOM files. DICOM files always come with metadata tags and the files are hierarchically organized as follows:
* Patient – Human or animal
* Study – A set of related imaging procedures
* Series – A single sequentially captured series of images
4. Advantages of using PACS in radiology
Apart from the medical image storing and sharing, PACS is instrumental in other aspects like:
4.1. Better organization of patient data
Until a couple of decades ago, patients had to carry their medical records to any health institution that they were visiting. This was mainly because, with every doctor consultation, new information such as prescriptions, examination reports, etc., is appended to the medical history. Maintaining medical reports on paper not only restricted sharing of information but also made it difficult to quickly search for necessary information.
PACS has made it possible to store and share images and patient information without the help of paper. Since images and patient information are stored in a more organized fashion in PACS, it makes it easier for radiologists and other healthcare professionals to access consulting records and the entire medical history of a patient within minutes, if not seconds, and that too with just a few clicks.
4.2. Increased access to patient data
One of the significant benefits of PACS is that it allows radiologists and physicians to access images and associated patient information from remote locations and devices. Particularly in the case of cloud softwares, radiologists don’t have to be on the premises to access a patient’s scan image and information. They can access, view, and assess images from any place, even from the convenience of their homes.
4.3. Better visualization of images
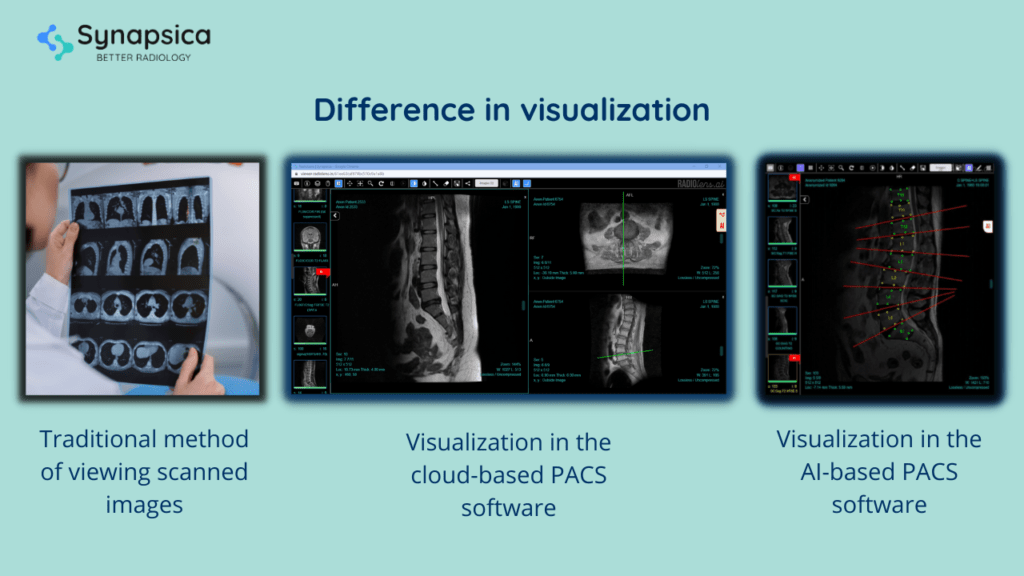
PACS provides an array of imaging tools like zoom, flip, pan, etc., using which any image can be electronically manipulated for better visualization. For instance, 2-D images can be converted into 3-D images for better visualization of organs, blood vessels, tissues, and bones. With better visualization, the chances of interpretation errors are limited and quick diagnosis is increased.
4.4. Cost saving
The use of radiological films is cost-prohibitive as they can be properly developed only with the help of chemicals. Not just chemicals, there are other elements like the equipment, products, films, room space to develop the image, etc., which makes the entire process costly. Whereas PACS is economical as there is no necessity to print the images.
5. Types of PACS
Just like another technology, PACS has undergone every phase of technology and germinated with different functionalities. Here’s a brief overview of the different types of PACS used in today’s healthcare sector.
5.1. Traditional PACS
Traditional PACS software stores patient digital images and associated information in a local storage model, where the server is directly connected to an array of hard drives and provides quick access to patient images and files. In traditional softwares, files are directly saved to the server as and when they are created.
As all the servers and associated hardware and software components are housed within the facility in a traditional PACS model, the healthcare provider has entire control and ownership over the framework, including the responsibility of operating and maintaining the PACS system.
Even though traditional softwares are quite outdated and are poised to become obsolete in the coming decades, it is still preferred by some health systems. If you are someone who is planning to establish a traditional PACS system for your institution, here are a couple of pointers that you must be wary about:
- Ensure that the storage capacity of the infrastructure is scalable, so you accommodate the increasing number of patient files effectively
- A well-thought contingency plan is essential for data recovery in traditional PACS in the case of unprecedented catastrophes like earthquakes and floods. While there are numerous backup options in traditional PACS systems, they could be expensive and require adequate management
- Initial setup costs for traditional PACS are high as the healthcare facility has to incur the preliminary hardware and software expenses
5.2. Cloud-based PACS
New-age PACS systems are cloud-based and the exact opposite of traditional one’s. Unlike traditional PACS where healthcare professionals need to be physically present on the premises to access patient data, cloud PACS allows users to store patient images and associated data from anywhere and anytime through the internet. In other words, cloud PACS facilitates remote working for radiologists.
In the cloud PACS model, the data is stored virtually which makes it easy to scale the storage space as per requirement. Also, in the cloud PACS system, the cloud vendor, who is also the PACS system vendor (in most cases), maintains all the hardware and software expenses at the offsite location. This means the user has to pay only for the internet connection and storage space used.
As cloud PACS allows users to access data remotely, physicians can effectively work on emergency cases, even if they are not physically present on the premises. Cloud PACS also facilitates quick and easy sharing of patient information during referrals.
The best part of cloud PACS is that it provides automated data recovery with no additional costs. Also, since the entire hosted cloud (which includes the servers, software, network, configuration, security, etc.) is replicated to a remote disaster recovery cloud, recovery from a disaster and restoration of systems and applications can be done swiftly.
Coming to the cost part, health systems can significantly cut capital as well as operating expenses with cloud PACS. Even expenses on maintenance and repair are considerably less when compared to traditional PACS.
5.3. AI-powered PACS
PACS systems have once again evolved with the emergence of the globe’s most-awaited technology AI or artificial intelligence.
While traditional and cloud PACS facilitate easy, quick, and remote sharing of patient images, AI goes a step further, and enables the system to automatically – store patient images against appropriate patient information, share images with referred radiologists/physicians, sort images based on their quality, prioritize cases, etc.
How AI-powered PACS will empower radiologists and health systems
The scope of AI in healthcare is increasing dramatically, particularly in radiology. Until a couple of years ago, the applications of AI were limited to cancer diagnosis and treatment. But the advent of COVID-19 brought to light how AI can simplify triaging, patient tracking and monitoring, and drug discovery.
While the pandemic has disrupted our lives in an unrecoverable way, it has also shown how technologies like artificial intelligence can enable healthcare professionals to provide optimal care at the right time. Most industry experts believe that the integration of AI with PACS will be inevitable and in the next 5 to 10 years PACS will be reinvented.
Here’s a preview of how AI-powered PACS will optimize radiology workflow;
5.3.1. Auto prioritization and allocation of cases
Radiologists perform numerous tasks before actually reading a patient’s image for deformities. One of those mundane tasks is prioritizing critical cases and allocating them to respective radiologists. Though this sounds like an easy task, it consumes a lot of radiologists’ productive hours.
With increasing dependency on medical images and the growing scarcity of radiologists, managing medical image data and timely diagnosis will be the biggest challenge for radiologists in the near future. However, such painful challenges can be avoided/overcome with AI.
AI-powered PACS can not only assist in managing medical image data, but also in prioritizing critical cases and allocating them as per a radiologist’s workload.
5.3.2. Improved image quality
Image quality has been a major issue for radiologists for decades. Poor quality images have been one of the primary reasons for misdiagnosis. This decades-long issue can be solved effortlessly with AI.
Just like how AI applications are boosting image quality in smartphones and other mobile devices, it can also boost image quality and resolution of medical images without losing information.
This will remove the need for patients to redo imaging tests for poor-quality images while enabling physicians to improve their image interpretation accuracy.
5.3.3. Auto-generation and sharing of reports
More than 60% of chest x-rays are normal without any abnormalities in a clinical setting. But radiologists will still have to manually create reports for the normal x-rays which is not an efficient use of their time. Besides helping in sorting normal images from abnormal ones, AI can also create preliminary reports justifying its action and share the same with referring physicians.
AI-enabled PACS solutions are gaining more attention in the current market, as healthcare is focusing on revamping workflows with AI. A real-time example that supports this fact is RADIOLens, an AI-enabled PACS solution engineered to optimize diagnostic workflow by automatically sorting bad quality images, creating preliminary reports, providing notifications, etc.
Favored by thousands across the globe, RADIOLens is used in more than 15 countries and handles over 1 million cases annually.
6. Which is the right PACS solution for my institution
As discussed above, modern-day PACS systems come with different functionalities and varying levels of security, which is exactly why it is confusing to choose the appropriate PACS solution for health systems.
Here are a couple of pointers that will help healthcare providers choose the right PACS software:
* First and foremost, have a clear business plan, particularly if you are focusing only on diagnostic services
* Establish milestones that will help you forecast your business growth, which is the key factor that helps in deciding the type of PACS system for your institution
* Diagnostic and imaging services, small and medium can opt for traditional or cloud PACS depending on their budget and requirement. Some institutions also go for hybrid PACS solutions (traditional + cloud), where cloud PACS are used to increase storage space once the physical servers are full. But, if you plan to expand your business across different geographies in the future, then AI-powered PACS is the right choice
* For service providers who are concerned about capital costs associated with PACS and are not sure about the required storage space for their institution, cloud PACS is the best option, as it allows users to scale the storage space as per requirement and users pay for only what they use without any hidden operational and maintenance cost
* For big-sized healthcare institutions that have numerous branches across geographies, moving to AI-powered PACS is a better solution, as they facilitate hassle-free operation and better patient care at an affordable price, which is often the key goal of large-scale health systems.
7. Impact of choosing the wrong PACS solution
Often diagnostic and imaging service providers, particularly the new and small-sized ones, go for traditional PACS systems as they feel that physical storage centers are more secure and easy to access. While this decision might seem beneficial during the initial days, in the long run, it might create more challenges than expected. This is mainly because the number of imaging procedures used is increasing exponentially as diagnostics are becoming highly dependent on medical images.
This also means that generation of patient images will be accelerated in the coming decade, and health institutions, small and big, should be prepared for the data explosion. For institutions relying on traditional PACS, such data explosions can be fatal and cost-prohibitive.
We live in the big data era today. So, health systems should make well-thought decisions and invest in advanced technologies like the cloud and AI that will help easily navigate the data tsunami that will be created by smart medical devices in the future.
9. Final thoughts
Diseases that were hard to diagnose and treat a decade ago, can now be easily identified and better treated with the help of technology. That is how much healthcare has evolved with time and technology.
Every service provider in the healthcare sector wants to make the best decision and investment for his institution, as he/she is well aware of the fact that ‘a patient’s life is at stake’, whenever they provide untimely or poor quality services.
Just like in the past, there will be new diseases and deformities evolving in this and the coming decades. While health institutions cannot do much about germinating diseases, what they can do is make the most of the breakthrough technologies like AI to provide timely and optimal patient care.
If you are one such health institution looking to provide timely and better quality services at an affordable rate, check out our AI-powered PACS, RADIOLens, built to streamline radiology workflows and enable quick diagnosis.

